RT-PCR lab
RT-PCR lab
You have a cell…is a certain gene on (by “on,” we mean active and producing mRNA?)?
If a certain gene is on when the cell divides, the gene might produce a protein that causes cell division….
Central Dogma:
DNA has genes and is in nucleus
TRANSCRIPTION: Double strands of DNA unwind to allow synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA) from one strand (the coding strand)
The mRNA moves out of the nucleus to the cytoplasm
mRNA binds to Ribosomes to code for a protein- protein made (translation)
Protein carries out intent of gene (red hair protein = hair gene)
DNA Structure
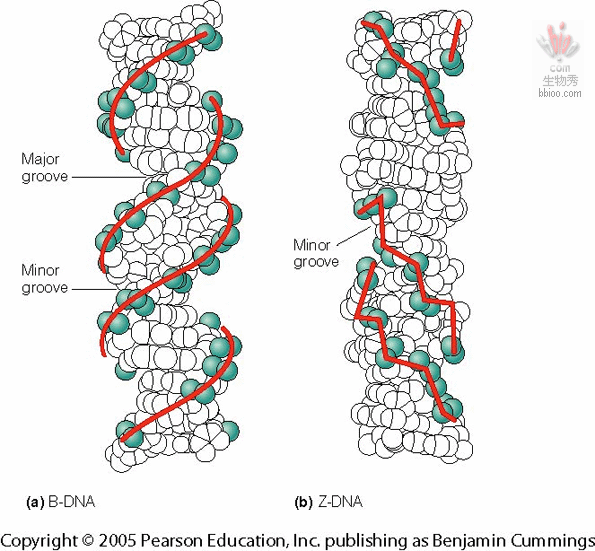
DNA is two strands of nucleotides Wrapped around each other in a double helix
We sequence the DNA to find out about the
genes present (later: bioinformatics lab)
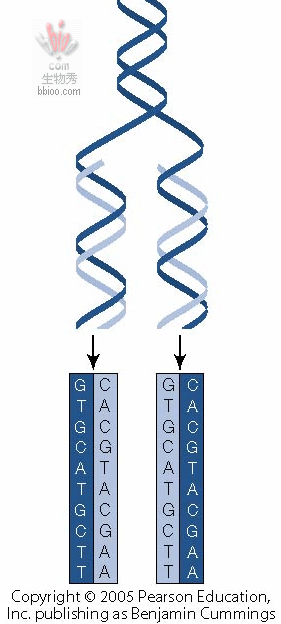
Unwind, mRNA is made off DNA template- similar to this picture of DNA made off of DNA.
Nucleotides pair up: G always pairs with C, T pairs with A. Except in RNA, T is replaced with U.
Transcription:RNA synthesis
(note coding and template strands) (ch.21)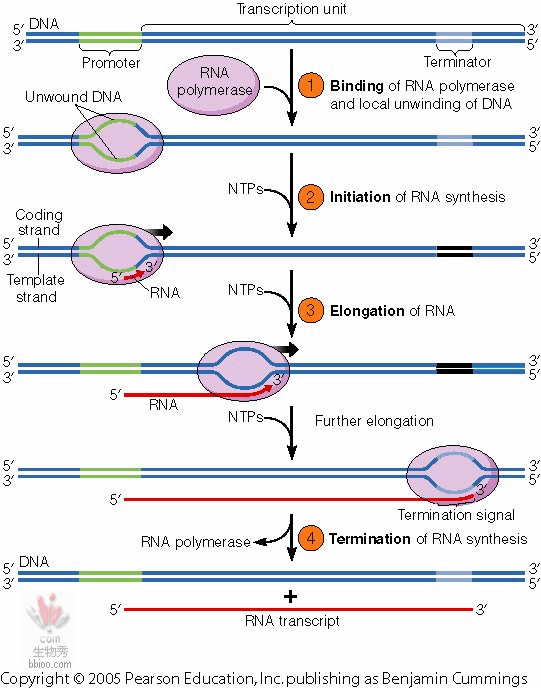
Making mRNA off DNA: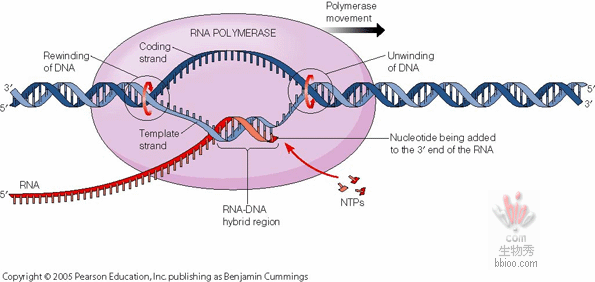
Transcription: Unwind 2 DNA strands and copy one making mRNA (ch.18)
So, first step of RT PCR is:
ISOLATE THE mRNA from the cell
Next, make DNA from the mRNA
This is reversing “transcription”– so use an enzyme originally obtained from viruses– ENZYME IS CALLED REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE (THE RT OF RT PCR)
Last slide: this is the RT part of RT PCR
PCR part:
After RT, you now have a tiny, trace amount of what is called complimentary DNA (cDNA). This tiny trace amount is not enough to sequence.
Next, you have to make enough copies of the tiny trace amount of cDNA to sequence
Steps in PCR (fig. 19A01):

Target sequence By using Specific primers To the target Sequence
Now repeat cycle over and over Get huge number of DNA copies --enough that you can now study The gene by sequencing it (finding Order of nucleotides)
PCR: polymerase chain reaction- making many copies of cDNA
View animation of PCR:
best:
http://www.dnalc.org/ddnalc/resources/shockwave/pcranwhole.html
OK:
http://users.ugent.be/~avierstr/principles/pcrani.html
http://www.people.virginia.edu/%7erjh9u/pcranim.html
http://www.abpischools.org.uk/resources/poster-series/pcr/pcranim.asp
PCR animation links
http://www.dna.utah.edu/PCR_Animation_Links.htm
Summary of RT PCR
RT-PCR animation
http://www.bio.davidson.edu/Courses/genomics/RTPCR/RT_PCR.html
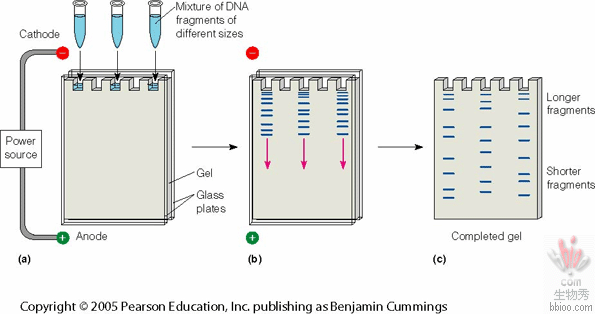
Electrophoresis to separate DNA by size (remember our prior discussion and animation): The fragment we want should be Of a known size!!